| Description |
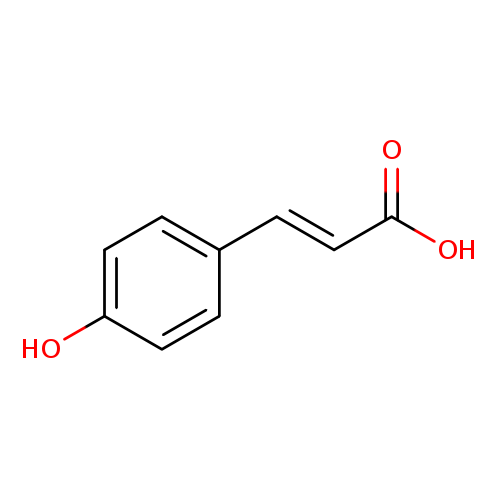
Trans-4-coumaric acid, also known as 4-hydroxycinnamic acid or trans-P-hydroxycinnamate, is a member of the class of compounds known as hydroxycinnamic acids. Hydroxycinnamic acids are compounds containing an cinnamic acid where the benzene ring is hydroxylated. Trans-4-coumaric acid is slightly soluble (in water) and a weakly acidic compound (based on its pKa). Trans-4-coumaric acid can be found in a number of food items such as garden onion, lowbush blueberry, german camomile, and garden rhubarb, which makes trans-4-coumaric acid a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Trans-4-coumaric acid can be found primarily in blood, feces, and urine, as well as in human fibroblasts tissue. Trans-4-coumaric acid exists in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to humans. |