| Description |
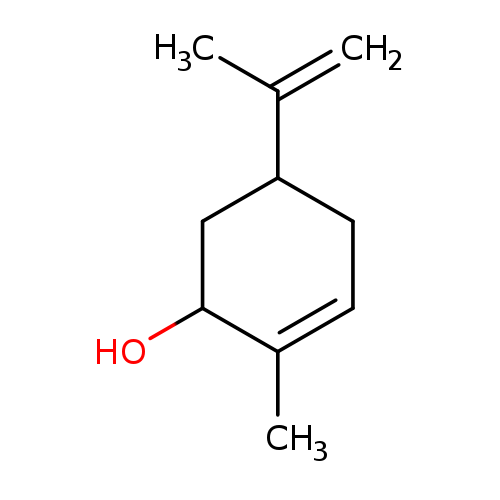
Carveol, also known as 5-isopropenyl-2-methyl-2-cyclohexen-1-ol or P-mentha-6,8-dien-2-ol, is a member of the class of compounds known as menthane monoterpenoids. Menthane monoterpenoids are monoterpenoids with a structure based on the o-, m-, or p-menthane backbone. P-menthane consists of the cyclohexane ring with a methyl group and a (2-methyl)-propyl group at the 1 and 4 ring position, respectively. The o- and m- menthanes are much rarer, and presumably arise by alkyl migration of p-menthanes. Carveol is slightly soluble (in water) and an extremely weak acidic compound (based on its pKa). Carveol is a caraway, fresh, and minty tasting compound and can be found in a number of food items such as green vegetables, citrus, lemon, and rocket salad (sspecies), which makes carveol a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Carveol is a natural unsaturated, monocyclic monoterpenoid alcohol that is a constituent of spearmint essential oil in the form of cis-(−)-carveol. It is a colorless fluid soluble in oils, but insoluble in water and has an odor and flavor that resemble those of spearmint and caraway. Consequently, it is used as a fragrance in cosmetics and as a flavor additive in the food industry . |