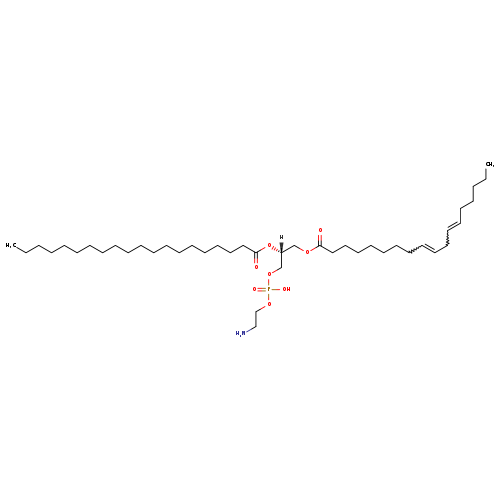
pe(18:2(9z,12z)/20:0)
| Name(s) | pe(18:2(9z,12z)/20:0) |
|---|---|
| Scientific name(s) | |
| Formula | C43H82NO8P |
| Molecular mass | 772.0868 |
| IUPAC name | (2-aminoethoxy)[(2R)-2-(icosanoyloxy)-3-(octadeca-9,12-dienoyloxy)propoxy]phosphinic acid |
| INCHI | InChI=1S/C43H82NO8P/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-19-20-22-24-26-28-30-32-34-36-43(46)52-41(40-51-53(47,48)50-38-37-44)39-49-42(45)35-33-31-29-27-25-23-21-18-16-14-12-10-8-6-4-2/h12,14,18,21,41H,3-11,13,15-17,19-20,22-40,44H2,1-2H3,(H,47,48)/t41-/m1/s1 |
| SMILE | [H][C@@](COC(=O)CCCCCCCC=CCC=CCCCCC)(COP(O)(=O)OCCN)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC |
| CAS ID | Not available |
| PubChem ID | 52924370 |
| DrugBank ID | Not available |
| CHEBI ID | Not available |
| Description | PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0) is a phosphatidylethanolamine (PE or GPEtn). It is a glycerophospholipid in which a phosphorylethanolamine moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site. As is the case with diacylglycerols, glycerophosphoethanolamines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached at the C-1 and C-2 positions. Fatty acids containing 16, 18 and 20 carbons are the most common. PE(18:2(9Z,12Z)/20:0), in particular, consists of one chain of linoleic acid at the C-1 position and one chain of arachidic acid at the C-2 position. The linoleic acid moiety is derived from seed oils, while the arachidic acid moiety is derived from peanut oil. Phospholipids, are ubiquitous in nature and are key components of the lipid bilayer of cells, as well as being involved in metabolism and signaling. While most phospholipids have a saturated fatty acid on C-1 and an unsaturated fatty acid on C-2 of the glycerol backbone, the fatty acid distribution at the C-1 and C-2 positions of glycerol within phospholipids is continually in flux, owing to phospholipid degradation and the continuous phospholipid remodeling that occurs while these molecules are in membranes. PEs are neutral zwitterions at physiological pH. They mostly have palmitic or stearic acid on carbon 1 and a long chain unsaturated fatty acid (e.g. 18:2, 20:4 and 22:6) on carbon 2. PE synthesis can occur via two pathways. The first requires that ethanolamine be activated by phosphorylation and then coupled to CDP. The ethanolamine is then transferred from CDP-ethanolamine to phosphatidic acid to yield PE. The second involves the decarboxylation of PS. [HMDB] |
|---|