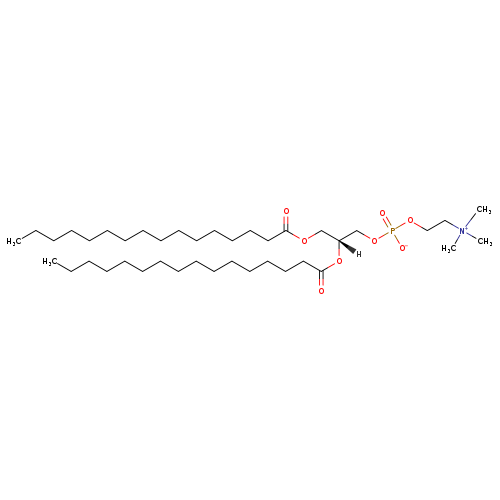
| Description |
PC(16:0/16:0) is a phosphatidylcholine (PC or GPCho). It is a glycerophospholipid in which a phosphorylcholine moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site. As is the case with diacylglycerols, glycerophosphocholines can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached at the C-1 and C-2 positions. Fatty acids containing 16, 18 and 20 carbons are the most common. PC(16:0/16:0), in particular, consists of two chains of palmitic acid at the C-1 and C-2 positions. The palmitic acid moieties are derived from fish oils, milk fats, vegetable oils and animal fats. Phospholipids, are ubiquitous in nature and are key components of the lipid bilayer of cells, as well as being involved in metabolism and signaling. Dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) is the major constituent of pulmonary surfactant. It is also used for research purposes in studying liposomes, lipid bilayers, and model biological membranes.
While most phospholipids have a saturated fatty acid on C-1 and an unsaturated fatty acid on C-2 of the glycerol backbone, the fatty acid distribution at the C-1 and C-2 positions of glycerol within phospholipids is continually in flux, owing to phospholipid degradation and the continuous phospholipid remodeling that occurs while these molecules are in membranes. PCs can be synthesized via three different routes. In one route, choline is activated first by phosphorylation and then by coupling to CDP prior to attachment to phosphatidic acid. PCs can also synthesized by the addition of choline to CDP-activated 1,2-diacylglycerol. A third route to PC synthesis involves the conversion of either PS or PE to PC. [HMDB] |