| Description |
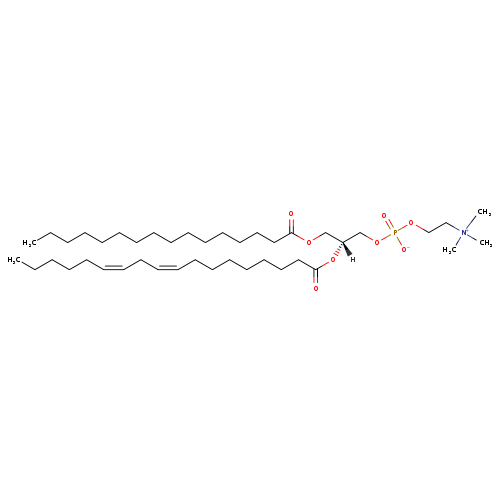
Palmitoyl-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine, also known as phosphatidylcholine(16:0/18:2) or pc(16:0/18:2), is a member of the class of compounds known as phosphatidylcholines. Phosphatidylcholines are glycerophosphocholines in which the two free -OH are attached to one fatty acid each through an ester linkage. Thus, palmitoyl-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine is considered to be a glycerophosphocholine lipid molecule. Palmitoyl-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine is practically insoluble (in water) and a moderately acidic compound (based on its pKa). Palmitoyl-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine can be found in a number of food items such as wax gourd, rowanberry, arrowroot, and chicory leaves, which makes palmitoyl-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Palmitoyl-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine can be found primarily in blood, saliva, and urine, as well as throughout all human tissues. In humans, palmitoyl-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine is involved in a couple of metabolic pathways, which include phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis PC(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)) and phosphatidylethanolamine biosynthesis PE(16:0/18:2(9Z,12Z)). Moreover, palmitoyl-linoleoyl phosphatidylcholine is found to be associated with schizophrenia. |