prodelphinidin b3
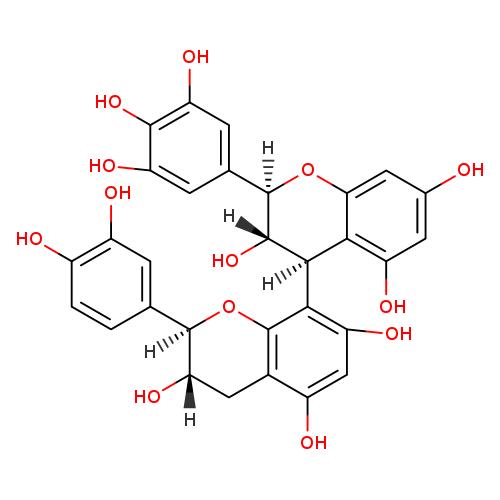
| Name(s) | prodelphinidin b3 |
|---|---|
| Scientific name(s) | |
| Formula | C30H26O14 |
| Molecular mass | 610.519 |
| IUPAC name | 8-[3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-4-yl]-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-1-benzopyran-3,5,7-triol |
| INCHI | InChI=1S/C30H26O14/c31-11-5-14(33)22-21(6-11)43-29(10-3-18(37)26(41)19(38)4-10)27(42)24(22)23-15(34)8-13(32)12-7-20(39)28(44-30(12)23)9-1-16(35)25(40)17(36)2-9/h1-6,8,20,24,27-29,31-42H,7H2 |
| SMILE | OC1CC2=C(O)C=C(O)C(C3C(O)C(OC4=CC(O)=CC(O)=C34)C3=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C3)=C2OC1C1=CC(O)=C(O)C(O)=C1 |
| CAS ID | 110115-59-8 |
| PubChem ID | Not available |
| DrugBank ID | Not available |
| CHEBI ID | Not available |
| Description | Prodelphinidin b3 is a member of the class of compounds known as biflavonoids and polyflavonoids. Biflavonoids and polyflavonoids are organic compounds containing at least two flavan/flavone units. These units are usually linked through CC or C-O-C bonds. Some examples include C2-O-C3, C2-O-C4, C3'-C3''', and C6-C8''. Prodelphinidin b3 is practically insoluble (in water) and a very weakly acidic compound (based on its pKa). Prodelphinidin b3 can be found in a number of food items such as broad bean, italian sweet red pepper, cucurbita (gourd), and green zucchini, which makes prodelphinidin b3 a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. |
|---|