| Description |
Present in apple, morello cherry, guava fruit, wine grapes, pineapple, crispbread, other breads, cheeses, wines, scallop and several essential oils, e.g. Roman chamomile. Acid and simple esters used as flavouring agents
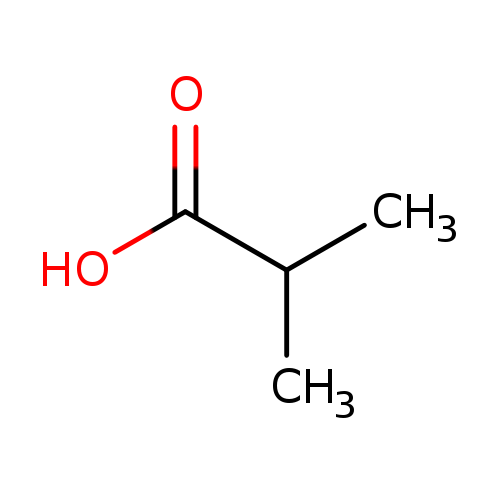
Isobutyric acid is a carboxylic or short chain fatty acid with characteristic sweat-like smell. Small amount of isobutyrate is generated via microbial (gut) metabolism. Small amounts may also be found in certain foods or fermented beverages. There is anosmia (genetic inability to smell) for the odor of isobutyric acid with a frequency of about 2.5%. (OMIM 207000). Isobutyric acid is slightly soluble in water but much more soluble in ethanol, ether and organic solvents. Isobutyric acid can affect people if breathed in and may be absorbed through the skin. Contact can irritate and burn the skin and eyes. Breathing Isobutyric acid can irritate the nose, throat and lungs causing coughing, wheezing and/or shortness of breath.; Isobutyric acid is an isomer of n-butyric acid; they have the same chemical formula C4H8 O2 but a different structure.; Isobutyric acid, also known as 2-methylpropanoic acid, is a carboxylic acid with structural formula (CH3)2-CH-COOH. It is found in the free state in carobs (Ceratonia siliqua) and in the root of Arnica dulcis, and as an ethyl ester in croton oil. |