guineensine; pipyahyine
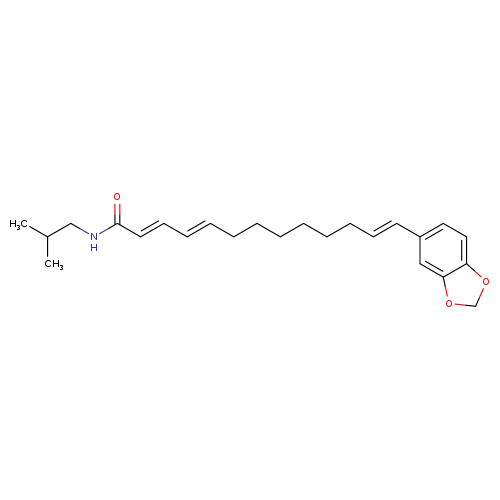
| Name(s) | guineensine; pipyahyine |
|---|---|
| Scientific name(s) | guineesine; pipyahyine; (2e,4e,12e)-13-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-n-(2-methylpropyl)trideca-2,4,12-trienamide; unii-7dk8dmu9jx; 7dk8dmu9jx; mls002473215; guineensine |
| Formula | C24H33NO3 |
| Molecular mass | 383.52372 |
| IUPAC name | (2E,4E,12E)-13-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)-N-(2-methylpropyl)trideca-2,4,12-trienamide |
| INCHI | InChI=1S/C24H33NO3/c1-20(2)18-25-24(26)14-12-10-8-6-4-3-5-7-9-11-13-21-15-16-22-23(17-21)28-19-27-22/h8,10-17,20H,3-7,9,18-19H2,1-2H3,(H,25,26)/b10-8+,13-11+,14-12+ |
| SMILE | CC(C)CNC(=O)\C=C\C=C\CCCCCC\C=C\C1=CC=C2OCOC2=C1 |
| CAS ID | 55038-30-7 |
| PubChem ID | 6442405 |
| DrugBank ID | Not available |
| CHEBI ID | Not available |
| Description | Guineensine, also known as pipyahyine, is a member of the class of compounds known as benzodioxoles. Benzodioxoles are organic compounds containing a benzene ring fused to either isomers of dioxole. Dioxole is a five-membered unsaturated ring of two oxygen atoms and three carbon atoms. Guineensine is practically insoluble (in water) and an extremely weak acidic compound (based on its pKa). Guineensine can be found in pepper (spice), which makes guineensine a potential biomarker for the consumption of this food product. Guineesine (or guineensine) is an alkaloid isolated from long pepper (Piper longum) and black pepper (Piper nigrum) . |
|---|