| Description |
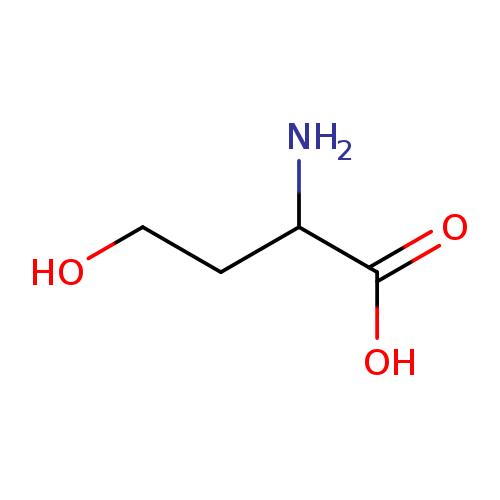
Homoserine, also known as L-isomer of homoserine or 2-amino-4-hydroxybutanoic acid, is a member of the class of compounds known as alpha amino acids. Alpha amino acids are amino acids in which the amino group is attached to the carbon atom immediately adjacent to the carboxylate group (alpha carbon). Homoserine is soluble (in water) and a moderately acidic compound (based on its pKa). Homoserine can be found in common pea and ginkgo nuts, which makes homoserine a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Homoserine (also called isothreonine) is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH2CH2OH. L-Homoserine is not one of the common amino acids encoded by DNA. It differs from the proteinogenic amino acid serine by insertion of an additional -CH2- unit into the backbone. Homoserine, or its lactone form, is the product of a cyanogen bromide cleavage of a peptide by degradation of methionine . |