| Description |
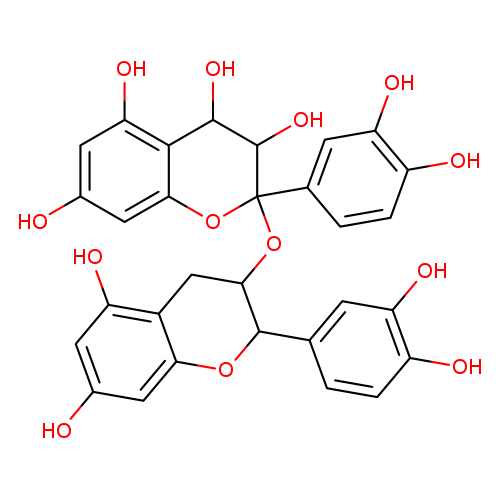
Procyanidin, also known as epicatechin-4alpha,8-epicatechin, is a member of the class of compounds known as catechins. Catechins are compounds containing a catechin moiety, which is a 3,4-dihydro-2-chromene-3,5.7-tiol. Procyanidin is practically insoluble (in water) and a very weakly acidic compound (based on its pKa). Procyanidin can be found in cloves, ginkgo nuts, and soursop, which makes procyanidin a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Procyanidins are members of the proanthocyanidin (or condensed tannins) class of flavonoids. They are oligomeric compounds, formed from catechin and epicatechin molecules. They yield cyanidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions . |