| Description |
Found in essential oils, e.g. neroli, rose oil, free and as estersand is also present in grapes, raspberry, strawberry, cherimoya, other fruits, cheddar cheese, Swiss cheese, wine, black tea, peated malt and other foodstuffs. Flavouring ingredient_x000D_
_x000D_
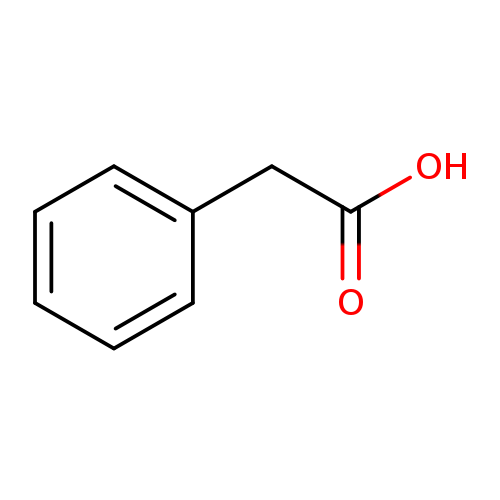
Phenyl acetate (or phenylacetate) is a carboxylic acid ester that has been found in the biofluids of patients with nephritis and/or hepatitis as well as patients with phenylketonuria (PKU). Excess phenylalanine in the body can be disposed of through a transamination process leading to the production of phenylpyruvate. The phenylpyruvate can be further metabolized into a number of products. Decarboxylation of phenylpyruvate gives phenylacetate, while a reduction reaction gives phenyllactate. The phenylacetate can be further conjugated with glutamine to give phenylacetyl glutamine. All of these metabolites can be detected in serum and urine of PKU patients. Phenyl acetate is also produced endogenously as the metabolite of 2-Phenylethylamine, which is mainly metabolized by monoamine oxidase to form phenyl acetate. 2-phenylethylamine is an "endogenous amphetamine" which may modulate central adrenergic functions, and the urinary phenyl acetate levels have been postulated as a marker for depression. (PMID: 17978765, 476920, 6857245). Phenylacetate is also found in essential oils, e.g. neroli, rose oil, free and as esters' and in many fruits. As a result it is used as a perfumery and flavoring ingredient.; Phenylacetic acid (abr. PAA and synonyms are: ?-toluic acid, benzeneacetic acid, alpha tolylic acid, 2-phenylacetic acid) is an organic compound containing a phenyl functional group and an acetic acid functional group. It is a white solid with a disagreeable odor. Because it is used in the illicit production of phenylacetone (used in the manufacture of meth/amphetamines), it is subject to controls in the United States. |