chrysanthemaxanthin
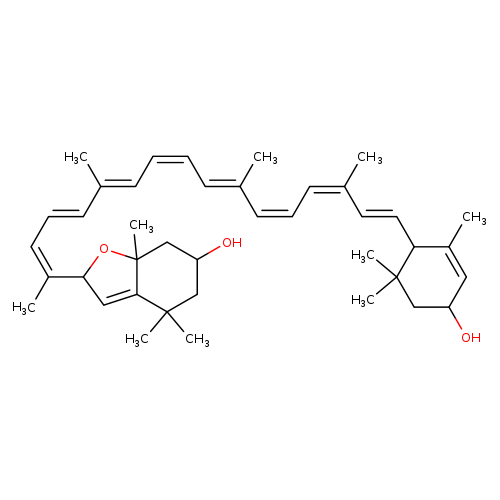
| Name(s) | chrysanthemaxanthin |
|---|---|
| Scientific name(s) | |
| Formula | C40H56O3 |
| Molecular mass | 584.8708 |
| IUPAC name | 2-[(2z,4e,6e,8z,10e,12z,14z,16e)-17-(4-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohex-2-en-1-yl)-6,11,15-trimethylheptadeca-2,4,6,8,10,12,14,16-octaen-2-yl]-4,4,7a-trimethyl-2,4,5,6,7,7a-hexahydro-1-benzofuran-6-ol |
| INCHI | InChI=1S/C40H56O3/c1-28(17-13-18-30(3)21-22-35-32(5)23-33(41)25-38(35,6)7)15-11-12-16-29(2)19-14-20-31(4)36-24-37-39(8,9)26-34(42)27-40(37,10)43-36/h11-24,33-36,41-42H,25-27H2,1-10H3/b12-11-,17-13-,19-14+,22-21+,28-15+,29-16+,30-18-,31-20- |
| SMILE | C\C(\C=C/C=C(/C)\C=C\C1C(C)=CC(O)CC1(C)C)=C/C=C\C=C(/C)\C=C\C=C(\C)C1OC2(C)CC(O)CC(C)(C)C2=C1 |
| CAS ID | 27780-11-6 |
| PubChem ID | 101298745 |
| DrugBank ID | Not available |
| CHEBI ID | Not available |
| Description | Flavoxanthin is a member of the class of compounds known as xanthophylls. Xanthophylls are carotenoids containing an oxygenated carotene backbone. Carotenes are characterized by the presence of two end-groups (mostly cyclohexene rings, but also cyclopentene rings or acyclic groups) linked by a long branched alkyl chain. Carotenes belonging form a subgroup of the carotenoids family. Xanthophylls arise by oxygenation of the carotene backbone. Flavoxanthin is practically insoluble (in water) and an extremely weak acidic compound (based on its pKa). Flavoxanthin can be found in a number of food items such as coffee and coffee products, ginkgo nuts, alcoholic beverages, and black elderberry, which makes flavoxanthin a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Flavoxanthin is a natural xanthophyll pigment with a golden-yellow color found in small quantities in a variety of plants. As a food additive it used under the E number E161a as a food coloring although it is not approved for use in the EU or USA. It is listed as food additive 161a in Australia and New Zealand where it is approved for usage as an ingredient in food products . |
|---|