lactose
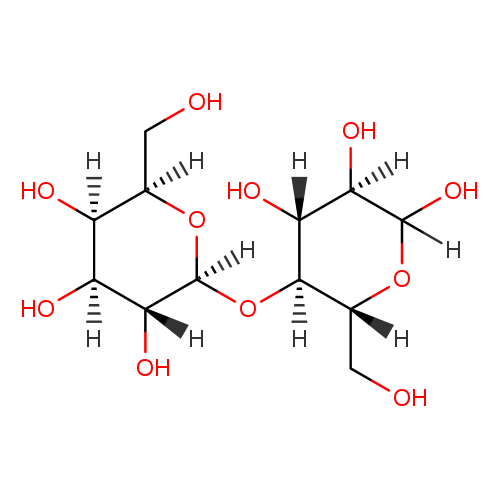
| Name(s) | lactose |
|---|---|
| Scientific name(s) | |
| Formula | C12H22O11 |
| Molecular mass | 342.2965 |
| IUPAC name | (2r,3r,4s,5r,6s)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-6-{[(2r,3s,4r,5r)-4,5,6-trihydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-3-yl]oxy}oxane-3,4,5-triol |
| INCHI | InChI=1S/C12H22O11/c13-1-3-5(15)6(16)9(19)12(22-3)23-10-4(2-14)21-11(20)8(18)7(10)17/h3-20H,1-2H2/t3-,4-,5+,6+,7-,8-,9-,10-,11?,12+/m1/s1 |
| SMILE | OC[C@H]1O[C@@H](O[C@H]2[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)C(O)O[C@@H]2CO)[C@H](O)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1O |
| CAS ID | 63-42-3 |
| PubChem ID | 84571 |
| DrugBank ID | DB04465 |
| CHEBI ID | 17716 |
| Description | Occurs in mammalian milk (human 6-7%, cow 4-5%), fruits of sapodilla Achras sapota, and a few other plants. Nutrient. obtained industrially from whey_x000D_ _x000D_ Lactose is a disaccharide sugar that is found most notably in milk and is formed from galactose and glucose. Lactose makes up around 2-8% of milk (by weight), although the amount varies among species and individuals. It is extracted from sweet or sour whey. [Wikipedia]. Lactose in the urine is a biomarker for the consumption of milk. Lactose is found in many foods, some of which are tortilla, swamp cabbage, scrapple, and spearmint. |
|---|