ellagic acid
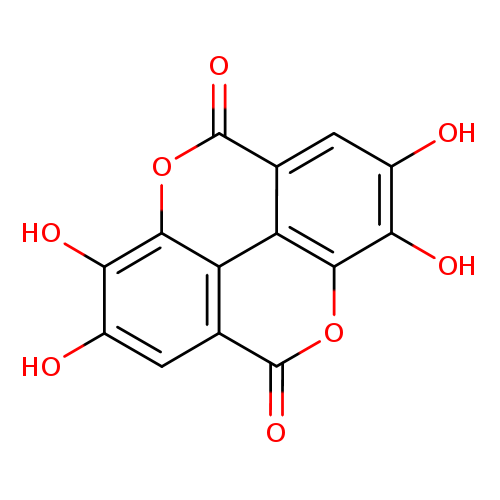
| Name(s) | ellagic acid |
|---|---|
| Scientific name(s) | benzoaric acid; lagistase; elagostasine; 2,3,7,8-tetrahydroxychromeno[5,4,3-cde]chromene-5,10-dione; eleagic acid; alizarine yellow |
| Formula | C14H6O8 |
| Molecular mass | 302.19264 |
| IUPAC name | 6,7,13,14-tetrahydroxy-2,9-dioxatetracyclo[6.6.2.04,16.011,15]hexadeca-1(15),4,6,8(16),11,13-hexaene-3,10-dione |
| INCHI | InChI=1S/C14H6O8/c15-5-1-3-7-8-4(14(20)22-11(7)9(5)17)2-6(16)10(18)12(8)21-13(3)19/h1-2,15-18H |
| SMILE | OC1=C(O)C2=C3C(=C1)C(=O)OC1=C3C(=CC(O)=C1O)C(=O)O2 |
| CAS ID | 476-66-4 |
| PubChem ID | 5281855 |
| DrugBank ID | DB08846 |
| CHEBI ID | Not available |
| Description | Widely distributed in higher plants especies dicotyledons. Intestinal astringent, dietary role disputed. Nutriceutical with anticancer and antioxidation props. Ellagic acid is a Polyphenol compound found in numerous fruits and vegetables, including, raspberries; Ellagic acid is a polyphenol antioxidant found in numerous fruits and vegetables including raspberries, strawberries, cranberries, walnuts, pecans, pomegranates and other plant foods. The antiproliferative and antioxidant properties of ellagic acid have spurred preliminary research into the potential health benefits of ellagic acid consumption.; and other plant foods. It is often regarded as an antioxidant. Ellagic Acid Clinical Tests on cultured human cells also show that Ellagic acid prevents the destruction of the p53 gene by cancer cells. Additional studies suggest that one of the mechanisms by which Ellagic acid inhibits mutagenesis and carcinogenesis is by forming adducts with DNA, thus masking binding sites to be occupied by the mutagen or carcinogen.; cranberries; pecans; pomegranates; strawberries; walnuts. |
|---|