uridine
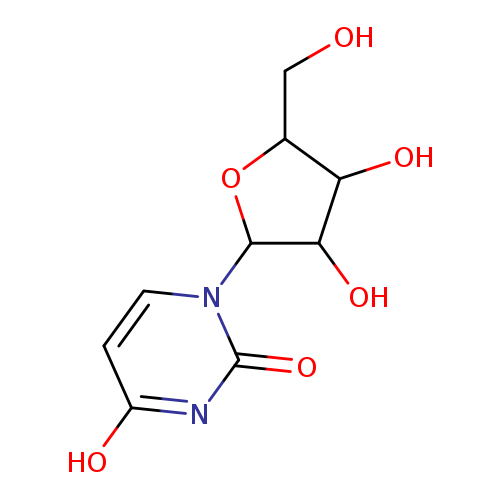
| Name(s) | uridine |
|---|---|
| Scientific name(s) | |
| Formula | C9H12N2O6 |
| Molecular mass | 244.203 |
| IUPAC name | 1-[3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydropyrimidine-2,4-dione |
| INCHI | InChI=1S/C9H12N2O6/c12-3-4-6(14)7(15)8(17-4)11-2-1-5(13)10-9(11)16/h1-2,4,6-8,12,14-15H,3H2,(H,10,13,16) |
| SMILE | OCC1OC(C(O)C1O)N1C=CC(O)=NC1=O |
| CAS ID | 58-96-8 |
| PubChem ID | 6029 |
| DrugBank ID | DB02745 |
| CHEBI ID | 16704 |
| Description | Uridine is a molecule (known as a nucleoside) that is formed when uracil is attached to a ribose ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a b-N1-glycosidic bond. ; Uridine is a molecule (known as a nucleoside) that is formed when uracil is attached to a ribose ring (also known as a ribofuranose) via a ?-N1-glycosidic bond. Uridine is found in many foods, some of which are celery leaves, canola, common hazelnut, and hickory nut. |
|---|