isoborneol; d-borneol
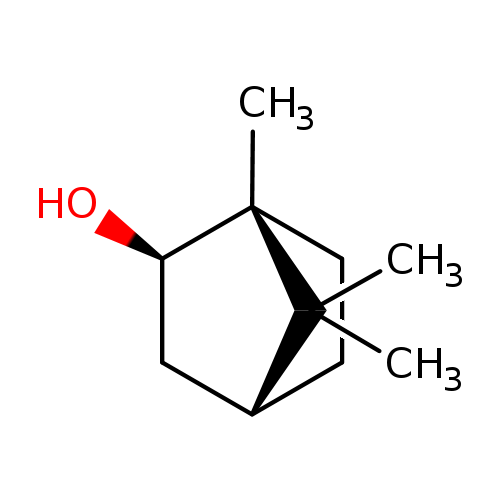
| Name(s) | isoborneol; d-borneol |
|---|---|
| Scientific name(s) | |
| Formula | C10H18O |
| Molecular mass | 154.2493 |
| IUPAC name | (1r,2r,4r)-1,7,7-trimethylbicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-2-ol |
| INCHI | InChI=1S/C10H18O/c1-9(2)7-4-5-10(9,3)8(11)6-7/h7-8,11H,4-6H2,1-3H3/t7-,8-,10+/m1/s1 |
| SMILE | CC1(C)[C@@H]2CC[C@@]1(C)[C@H](O)C2 |
| CAS ID | 464-43-7; 124-76-5 |
| PubChem ID | 439568 |
| DrugBank ID | Not available |
| CHEBI ID | Not available |
| Description | (-)-isoborneol, also known as isoborneol, (1r-endo)-isomer, is a member of the class of compounds known as bicyclic monoterpenoids. Bicyclic monoterpenoids are monoterpenoids containing exactly 2 rings, which are fused to each other (-)-isoborneol is practically insoluble (in water) and an extremely weak acidic compound (based on its pKa). Within the cell, (-)-isoborneol is primarily located in the membrane (predicted from logP). It can also be found in the extracellular space. |
|---|