| Description |
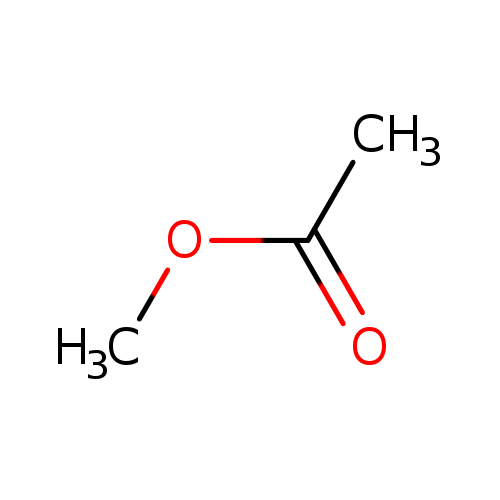
Methyl acetate is an ester that is synthesized from acetic acid and methanol in the presence of strong acids such as sulfuric acid in an esterification reaction. In the presence of strong bases such as sodium hydroxide or strong acids such as hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid it is hydrolyzed back into methanol and acetic acid, especially at elevated temperature.; Methyl acetate, also known as acetic acid methyl ester or methyl ethanoate, is a clear, flammable liquid with a characteristic, not unpleasant smell like certain glues or nail polish removers. Methyl acetate has characteristics very similar to its analog ethyl acetate. Methyl acetate is used as a solvent in glues, paints, and nail polish removers, in chemical reactions, and for extractions. Methyl acetate is a non-polar (lipophilic) to weakly polar (hydrophilic) aprotic solvent. Methyl acetate has a solubility of 25% in water at room temperature. At elevated temperature its solubility in water is much higher. Methyl acetate is not stable in the presence of strong aqueous bases or acids. Methyl acetate is VOC exempt.; The conversion of methyl acetate back into its components, by an acid, is a first-order reaction with respect to the ester. The reaction of methyl acetate and a base, for example sodium hydroxide, is a second-order reaction with respect to both reactants. Methyl acetate is a flavouring agent and can be found in many foods, some of which are apple, grape, banana, orange mint, and ginger. |