| Description |
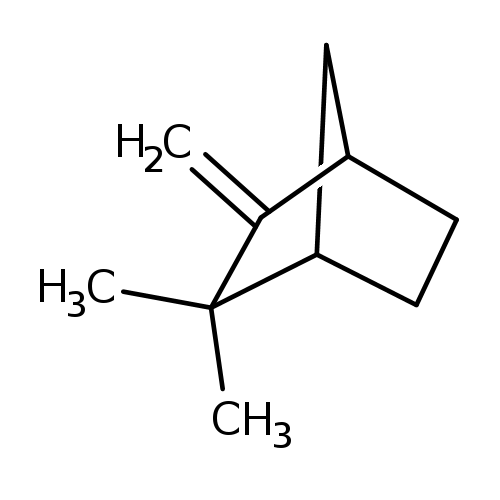
Camphene, also known as 2,2-dimethyl-3-methylenebicyclo[2.2.1]heptane or 2,2-dimethyl-3-methylenenorbornane, is a member of the class of compounds known as bicyclic monoterpenoids. Bicyclic monoterpenoids are monoterpenoids containing exactly 2 rings, which are fused to each other. Camphene is a camphor, fir needle, and herbal tasting compound and can be found in a number of food items such as cardamom, yellow bell pepper, common thyme, and coriander, which makes camphene a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Camphene can be found primarily in feces and saliva. Camphene exists in all eukaryotes, ranging from yeast to humans. Camphene is a bicyclic monoterpene. It is nearly insoluble in water, but very soluble in common organic solvents. It volatilizes readily at room temperature and has a pungent smell. It is a minor constituent of many essential oils such as turpentine, cypress oil, camphor oil, citronella oil, neroli, ginger oil, and valerian. It is produced industrially by catalytic isomerization of the more common alpha-pinene. Camphene is used in the preparation of fragrances and as a food additive for flavoring. Its mid-19th century use as a fuel for lamps was limited by its explosiveness . |