| Description |
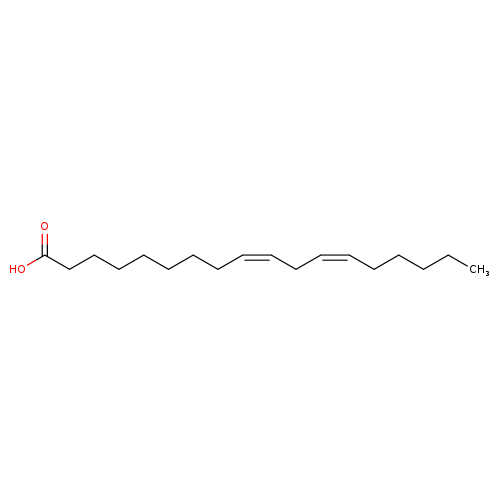
Linoleate, also known as (9z,12z)-octadecadienoic acid or cis,cis-linoleic acid, belongs to lineolic acids and derivatives class of compounds. Those are derivatives of lineolic acid. Lineolic acid is a polyunsaturated omega-6 18 carbon long fatty acid, with two CC double bonds at the 9- and 12-positions. Thus, linoleate is considered to be a fatty acid lipid molecule. Linoleate is practically insoluble (in water) and a weakly acidic compound (based on its pKa). Linoleate can be found in a number of food items such as kiwi, chinese cabbage, common bean, and butternut, which makes linoleate a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Linoleate can be found primarily in most biofluids, including feces, blood, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and saliva, as well as throughout most human tissues. In humans, linoleate is involved in the alpha linolenic acid and linoleic acid metabolism. Moreover, linoleate is found to be associated with hypertension, essential hypertension, schizophrenia, and gestational diabetes. Linoleate is a non-carcinogenic (not listed by IARC) potentially toxic compound. Linoleic acid (LA), a carboxylic acid, is a polyunsaturated omega-6 fatty acid, an 18-carbon chain with two double bonds in cis configuration. A shorthand notation like "18:2 (n-6)" or "18:2 cis-9,12" may be used in literature. It typically occurs in nature as a triglyceride ester; free fatty acids are typically low in foods . |