| Description |
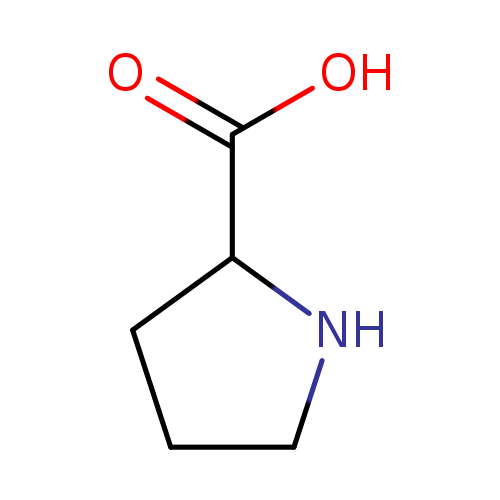
Proline, also known as dl-proline or hpro, belongs to proline and derivatives class of compounds. Those are compounds containing proline or a derivative thereof resulting from reaction of proline at the amino group or the carboxy group, or from the replacement of any hydrogen of glycine by a heteroatom. Proline is soluble (in water) and a moderately acidic compound (based on its pKa). Proline can be found in a number of food items such as yellow zucchini, swiss chard, spinach, and cucumber, which makes proline a potential biomarker for the consumption of these food products. Proline (abbreviated as Pro or P; encoded by the codons CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated NH2+ form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain pyrrolidine, classifying it as a nonpolar (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans, meaning the body can synthesize it from the non-essential amino acid L-glutamate . |