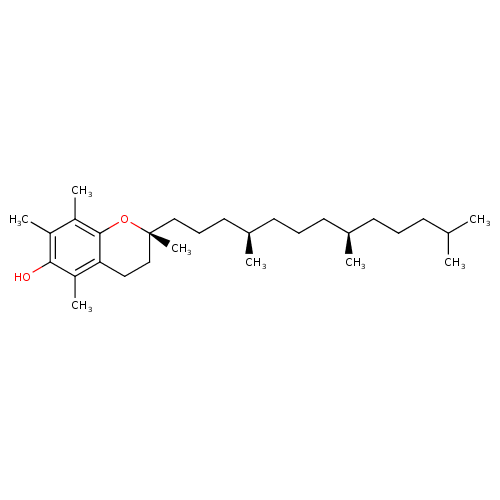
| Name(s) |
α-tocopherol; vitamin e; alpha-tocopherol |
| Scientific name(s) |
vitamin e; alpha-tocopherol; d-alpha-tocopherol; (+)-alpha-tocopherol; 5,7,8-trimethyltocol; aquasol e; tocopherol |
| Formula |
C29H50O2 |
| Molecular mass |
430.717 |
| IUPAC name |
(2r)-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-[(4r,8r)-4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl]-3,4-dihydrochromen-6-ol |
| INCHI |
InChI=1S/C29H50O2/c1-20(2)12-9-13-21(3)14-10-15-22(4)16-11-18-29(8)19-17-26-25(7)27(30)23(5)24(6)28(26)31-29/h20-22,30H,9-19H2,1-8H3/t21-,22-,29-/m1/s1 |
| SMILE |
CC(C)CCC[C@@H](C)CCC[C@@H](C)CCC[C@]1(C)CCC2=C(O1)C(C)=C(C)C(O)=C2C |
| CAS ID |
[59-02-9]; 10191-41-0; 59-02-9 |
| PubChem ID |
14985 |
| DrugBank ID |
DB00163 |
| CHEBI ID |
Not available |