| Description |
Present in fruits and other plant materials. Nutrient supplement. Vitamin, enzyme cofactor [DFC]_x000D_
_x000D_
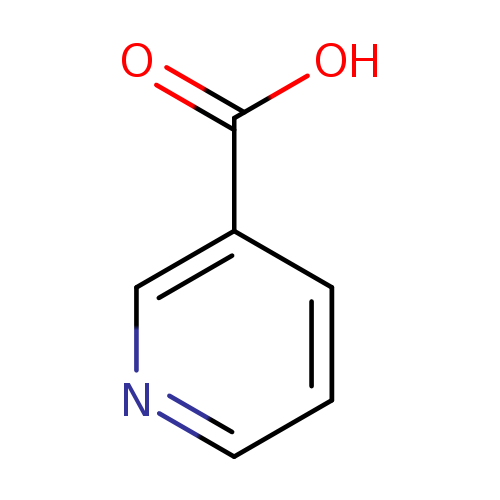
Niacin (also known as vitamin B3, nicotinic acid and vitamin PP) is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NO2 and, depending on the definition used, one of the forty to eighty essential human nutrients. This colorless, water-soluble solid is a derivative of pyridine, with a carboxyl group (COOH) at the 3-position. Other forms of vitamin B3 include the corresponding amide, nicotinamide ("niacinamide"), where the carboxyl group has been replaced by a carboxamide group (CONH2), as well as more complex amides and a variety of esters. The terms niacin, nicotinamide, and vitamin B3 are often used interchangeably to refer to any member of this family of compounds, since they have the same biochemical activity. [Wikipedia]. Nicotinic acid is found in many foods, some of which are cold cut, garden onion (variety), napa cabbage, and horseradish tree. |