| Description |
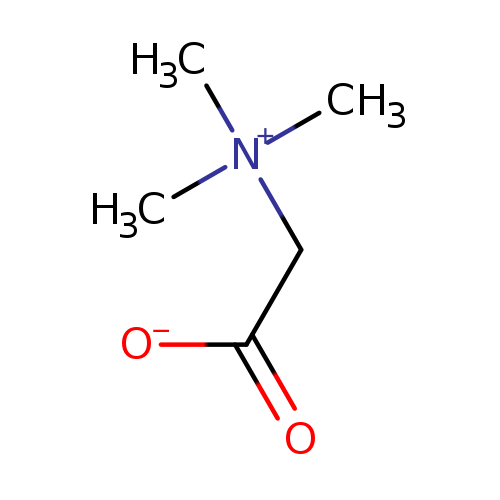
Betaine or trimethylglycine is a methylated derivative of glycine. It functions as a methyl donor in that it carries and donates methyl functional groups to facilitate necessary chemical processes. The donation of methyl groups is important to proper liver function, cellular replication, and detoxification reactions. Betaine also plays a role in the manufacture of carnitine and serves to protect the kidneys from damage. Betaine has also been of interest for its role in osmoregulation. As a drug, betaine hydrochloride has been used as a source of hydrochloric acid in the treatment of hypochlorhydria. Betaine has also been used in the treatment of liver disorders, for hyperkalemia, for homocystinuria, and for gastrointestinal disturbances. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th Ed, p1341). Betaine is found in many foods, some of which are potato puffs, poppy, hazelnut, and garden cress. |